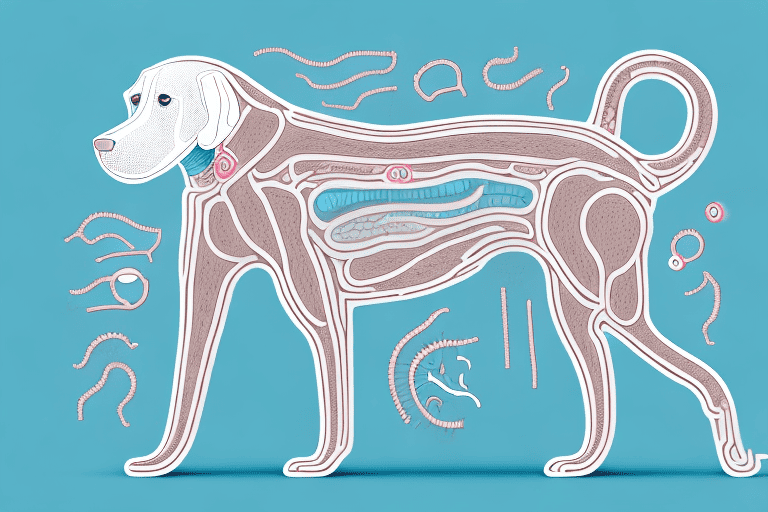
Dogs, like humans, have a specialized digestive system that enables them to break down and absorb nutrients from their food. Understanding the canine digestive system is crucial for dog owners to ensure their pet’s overall health and well-being.
Understanding the Canine Digestive System
The Role of the Dog’s Mouth in Digestion
Digestion begins in a dog’s mouth. Their mouth plays a crucial role in the initial breakdown of food. Dogs have sharp, pointed teeth designed for tearing and chewing. The action of chewing helps to mechanically break down the food into smaller particles, making it easier to swallow and digest.
Additionally, the dog’s saliva contains enzymes that start the chemical process of digestion. These enzymes begin breaking down starches into simpler sugars, preparing the food for further digestion in the stomach and intestines.
Did you know that a dog’s mouth is also home to a variety of bacteria? These bacteria play a role in maintaining oral health and preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms. Regular dental care, such as brushing your dog’s teeth and providing dental chews, can help keep their mouth clean and healthy.
The Importance of the Esophagus in Dog Digestion
Once the food is chewed and mixed with saliva, it travels down the esophagus, a muscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach. The esophagus contracts in coordinated waves, known as peristalsis, to push the food towards the stomach. Dogs have a relatively short esophagus, contributing to a faster digestion process compared to some other animals.
Interestingly, the esophagus has a special structure called the lower esophageal sphincter. This sphincter acts as a valve, preventing stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus and causing heartburn or acid reflux. This mechanism helps to protect the delicate lining of the esophagus from damage.
The Function of the Dog’s Stomach in Digestion
Upon reaching the stomach, food mixes with gastric juices to further break it down. The stomach’s muscular walls contract to churn and mix the partially digested food, forming a semi-fluid mixture called chyme. Gastric acid in the stomach helps to kill bacteria and provide an acidic environment for enzyme activity. The stomach also plays a significant role in regulating the rate at which food enters the small intestine for further digestion.
Did you know that a dog’s stomach can expand significantly to accommodate larger meals? This ability is especially important for dogs in the wild, as they may need to consume large amounts of food in one sitting to sustain themselves until their next meal. However, it’s essential to feed dogs an appropriate portion size to prevent overeating and potential digestive issues.
The Role of the Small Intestine in Dog Digestion
The small intestine is where most of the crucial nutrient absorption takes place. The semi-digested chyme from the stomach enters the small intestine, where bile from the liver and enzymes from the pancreas further break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. The lining of the small intestine contains finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area available for nutrient absorption into the bloodstream.
Through a complex process, nutrients like amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals are absorbed into the bloodstream to provide energy and support vital bodily functions.
Did you know that the small intestine of a dog can be several times longer than its body? This long and convoluted structure allows for maximum nutrient absorption. It also highlights the importance of providing dogs with a balanced and nutritious diet to ensure they receive all the essential nutrients they need for optimal health.
The Function of the Large Intestine in Dog Digestion
After the small intestine absorbs most of the nutrients, any undigested food, water, and waste products pass into the large intestine. The large intestine’s primary function is to absorb water and electrolytes, reabsorbing them back into the body. The large intestine also houses a diverse community of bacteria, known as the gut microbiota, which plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health and overall well-being.
Finally, the waste materials, now in the form of feces, are stored in the rectum until they are expelled from the body through the anus.
Did you know that the gut microbiota in a dog’s large intestine consists of trillions of bacteria? These bacteria help break down certain indigestible fibers, produce essential vitamins, and support the immune system. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota is vital for a dog’s overall well-being, and a balanced diet rich in fiber can promote a thriving gut environment.
Unique Features of a Dog’s Digestive System
Dogs have a fascinating digestive system that is uniquely designed to efficiently process their food and extract the necessary nutrients. Understanding the various aspects of a dog’s digestive system can help us ensure their overall health and well-being.
Speed of Digestion in Dogs
Compared to some other animals, dogs have a relatively short digestive transit time. This means that the entire process of digestion, from the time food is consumed to the elimination of waste, occurs more quickly in dogs. The rapid digestion in dogs allows them to efficiently extract nutrients from their food.
When a dog consumes food, it travels down the esophagus and enters the stomach, where the initial breakdown begins. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and acids that help break down the food into smaller particles. From there, the partially digested food moves into the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption takes place. The small intestine is lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for nutrient absorption.
As the food continues its journey through the small intestine, the nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to various parts of the body to support vital functions. The remaining undigested waste then enters the large intestine, where water is absorbed, and the waste is formed into feces before being eliminated through the rectum and anus.
The Impact of Diet on a Dog’s Digestive Health
A dog’s diet plays a significant role in maintaining optimal digestive health. Dogs are primarily carnivorous, but they have adapted to digest and utilize plant-based foods as well. A balanced diet that meets a dog’s nutritional requirements is essential for proper digestion.
High-quality commercially prepared dog food or appropriately formulated homemade diets can provide the necessary nutrients for a healthy digestive system. These diets often contain a combination of animal proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals that are carefully balanced to support a dog’s overall health. It is important to choose a diet that is appropriate for your dog’s age, breed, size, and specific dietary needs.
In addition to providing a balanced diet, it is also important to consider the feeding schedule and portion sizes. Feeding your dog smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help prevent digestive issues such as bloating and indigestion. It is always best to consult with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable diet and feeding routine for your dog.
The Role of Bacteria in a Dog’s Gut
The gut microbiota, a colony of beneficial bacteria residing in a dog’s gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in digestion and overall health. These bacteria not only aid in the breakdown of certain nutrients but also support the immune system and help prevent harmful bacteria from colonizing the gut.
When a dog consumes food, the gut microbiota helps break down complex carbohydrates, fibers, and other components that the dog’s own digestive enzymes may struggle to process. This symbiotic relationship between the dog and the bacteria allows for better nutrient absorption and overall digestive efficiency.
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota through proper diet and occasional administration of probiotics is important for a dog’s digestive well-being. Probiotics are live bacteria or yeasts that can be beneficial to the gut microbiota. They can help restore the balance of gut bacteria, especially after a course of antibiotics or during times of digestive upset.
It is worth noting that sudden changes in diet or the administration of certain medications can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota, leading to digestive issues such as diarrhea or constipation. Therefore, it is important to introduce dietary changes gradually and consult with a veterinarian before making any significant alterations to your dog’s diet.
In conclusion, a dog’s digestive system is a complex and remarkable mechanism that allows them to efficiently process and extract nutrients from their food. By understanding the unique features of their digestive system, we can make informed decisions about their diet and overall digestive health, ensuring they lead happy and healthy lives.
Common Digestive Issues in Dogs
Symptoms of Digestive Problems in Dogs
Dogs may experience various digestive issues that can affect their overall health and well-being. Common symptoms of digestive problems in dogs include vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, excessive gas, abdominal discomfort, and loss of appetite. If these symptoms persist or worsen, it is essential to seek veterinary attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Digestive Issues in Dogs
There are several factors that can contribute to digestive problems in dogs. These include dietary indiscretions, such as consuming spoiled or inappropriate food, food allergies or sensitivities, intestinal parasites, bacterial or viral infections, certain medications, stress, and underlying medical conditions.
Treatment and Prevention of Digestive Problems
Treatment for digestive issues in dogs depends on the underlying cause. In many cases, dietary changes, such as transitioning to a more easily digestible diet or eliminating allergenic ingredients, can help resolve the problem. Other treatment options may include medication, probiotics, deworming medications, or addressing any underlying medical conditions. Prevention of digestive problems in dogs involves providing a balanced diet, regular veterinary check-ups, and avoiding exposure to potentially harmful substances.
The Impact of Age on a Dog’s Digestive System
Digestive System of Puppies
During the early stages of life, puppies have a delicate digestive system that requires special attention. They rely on their mother’s milk, which provides essential nutrients and antibodies to support their growth and development. As they transition to solid food, a gradual introduction of age-appropriate puppy food is necessary to prevent digestive upset.
Changes in Digestion as Dogs Age
As dogs age, their digestive system undergoes natural changes. Older dogs may experience reduced efficiency in nutrient absorption and decreased enzyme production. This can result in a decreased ability to digest certain nutrients properly. Adjusting the diet to meet the changing needs of older dogs, including easily digestible proteins and appropriate fiber levels, can help support their aging digestive system.
Maintaining Digestive Health in Senior Dogs
Regular veterinary check-ups and tailored nutrition are crucial for maintaining digestive health in senior dogs. A veterinarian can recommend specific diets or supplements to address age-related digestive issues. Additionally, providing ample fresh water, regular exercise, and managing stress levels can also support the overall digestive well-being of older dogs.
In conclusion, dogs have a complex digestive system that allows them to efficiently break down and absorb nutrients from their food. Understanding the various components and functions of a dog’s digestive system is integral to providing optimal care and maintaining their overall health and well-being. By providing a balanced diet, addressing digestive issues promptly, and adjusting their care as they age, dog owners can help ensure a healthy digestive system for their beloved pets.
Transform Your Dog’s Digestive Health into Art with My Good Doggo
While you’re taking care of your dog’s digestive health, why not celebrate their unique personality in a fun and artistic way? With My Good Doggo, you can turn your furry friend’s photo into a delightful piece of art. Choose from various artistic styles and watch as our AI transforms your dog into a whimsical masterpiece. It’s a perfect way to share the love and joy your dog brings to your life. Use the My Good Doggo App today and start creating and sharing your dog’s AI-generated artwork with the world!